KöMaL Problems in Physics, October 2023
Please read the rules of the competition.
Show/hide problems of signs:
 |
Problems with sign 'M'Deadline expired on November 15, 2023. |
M. 425. Measure as accurately as possible the density of the material of a footed glass or any other type of drinking glass.
(6 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'G'Deadline expired on November 15, 2023. |
G. 825. We have a round wall clock with no numbers or graduations on the ``dial'', just hands.
The hour and the minute hands can only be adjusted by a knob at the back. At the back there is a circular rim which allows the clock to be hung on the wall in any position. How many different positions can it be placed on the wall so that it will keep good time when properly adjusted?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 826. In the morning rush hour a car travels at half of the urban speed limit for half an hour (the urban speed limit in Hungary is 50 km/h), then reaching the motorway it travels at three quarters of the speed limit on the motorway for 4 hours (speed limit on motorways: 130 km/h). Finally it travels for two hours on a single carriageway at 80% of the speed limit there (the speed limit on a single carriageway is 90 km/h). What is the average speed of the car?
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 827. The sequence of images shows the stages of a water droplet falling from a dripping tap. Describe what is happening in each picture. (See the attached figure.)
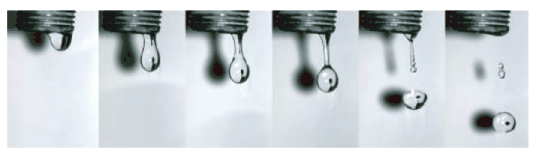
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 828. Assume that the Earth is a perfect sphere, with a spherically symmetric mass distribution, and with a radius of 6400 km. Its mass is the same as that of the real Earth and the period of its rotation about its axis is also the same as the period of the Earth. A stout physicist at the North Pole measures his mass with a bathroom scale, which is accurate to 10 grams, and reads 100.00 kg. How much would the same scale read if he measured himself at the equator?
(3 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'P'Deadline expired on November 15, 2023. |
P. 5508. Starting from rest, a car accelerates uniformly to a speed of \(\displaystyle v_0\). Along the acceleration track, a lot of speedometers were installed, at equal distances between two neighbouring ones. What is the average of readings of the speedometers?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5509. A small rubber bullet was fired with a toy rifle, from a point close to the horizontal ground, such that the greatest height that the bullet reached was equal to the horizontal range of its path.
\(\displaystyle a)\) At what angle, measured from the horizontal, was the bullet fired?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What are these distances if the initial speed of the bullet was 10 m/s?
\(\displaystyle c)\) What is the radius of curvature of the trajectory at the moment right after the launch and at the highest point of the trajectory?
(Neglect air resistance.)
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5510. A trolleybus leaves the stop with an acceleration of \(\displaystyle 1~\mathrm{m/s}^2\). A student standing on one leg is holding the vertical bus handle at a height of 1.5 m in front of him, in the direction of travel. With what horizontal force does the 75 kg person pull the handle to maintain his vertical position? The centre of gravity of the man is 1 m above the floor of the bus.
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5511. Point-like weights of masses \(\displaystyle m\) and \(\displaystyle M=2m\) are attached to the two endpoints of the diameter of a circular ring of radius \(\displaystyle R\) and of negligible mass. The ring is placed on a tabletop so that it lies in a vertical plane and the weights are along the same vertical line, initially the heavier is above the other, as shown in the figure. The ring is released from this unstable equilibrium state. The friction between the ring and the tabletop is sufficiently high to allow the ring to roll on the tabletop without slipping.
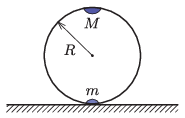
\(\displaystyle a)\) What is the speed of the centre of the ring when the weight of \(\displaystyle M\) reaches the lowest point of its trajectory?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the downward force exerted on the table in case \(\displaystyle a)\)?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5512. A certain amount of water is heated from \(\displaystyle 20\;{}^\circ\)C to \(\displaystyle 40\;{}^\circ\)C using an 800 W immersion heater. We expect to heat the water in 210 seconds, but instead we find that it takes 230 seconds. Determine the heat capacity of the vessel. (Ignore other heat losses.)
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5513. Using two convex lenses we can build a (Keplerian) telescope. We can also build a (Galilean) telescope with using one convex and one concave lens. Can we build a telescope with two concave lenses?
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5514. A point-like body with a charge \(\displaystyle -Q<0\) is fixed at point \(\displaystyle A\), which lies in a horizontal plane. In this plane, there is another point-like body of mass \(\displaystyle m\), and with charge \(\displaystyle q>0\) which can move without friction. Initially, the body of mass \(\displaystyle m\) is at point \(\displaystyle B\), and at this moment the initial distance of the charges is \(\displaystyle r_0\), and the body of mass \(\displaystyle m\) has a velocity of magnitude \(\displaystyle v_0=\sqrt{\frac{kqQ}{mr_0}}\), perpendicular to the line segment \(\displaystyle AB\) and parallel to the plane, as shown in the figure.
(The magnitude of the charges does not change during the motion.)
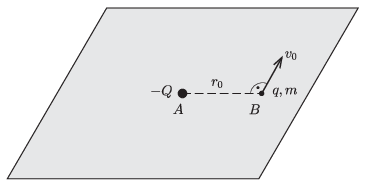
\(\displaystyle a)\) How much time elapses until the moving body returns to the line defined by the points \(\displaystyle AB\)?
\(\displaystyle b)\) Now the initial velocity of the moving body is halved. By what factor should the previously determined time be multiplied in order to get the time during which the moving body first reaches its furthest point from its initial position?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5515. According to the Bohr model, at what fraction of the speed of light does the electron move in the ground state of the hydrogen atom?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5516. A ping-pong ball, spinning around a horizontal axis, falls vertically onto the tabletop. The ball, which can be considered as a thin spherical shell, has a mass of \(\displaystyle m\), a radius of \(\displaystyle R\), its speed at the impact is \(\displaystyle v_0\), its angular speed is \(\displaystyle \omega_0=v_0/R\), and its moment of inertia is \(\displaystyle \Theta=\frac23 mR^2\). Both the coefficients of kinetic and static friction are \(\displaystyle \mu\). Consider the collision to be instantaneous and perfectly elastic (i.e. right before and after the collision the components of the velocity of the ball, which are perpendicular to the table, should be equal in magnitude.)
What will be the magnitude and the direction of the velocity of the ball after the collision? What will be its the angular speed?
(6 pont)
Upload your solutions above.
