KöMaL Problems in Physics, December 2023
Please read the rules of the competition.
Show/hide problems of signs:
 |
Problems with sign 'M'Deadline expired on January 15, 2024. |
M. 427. In physics classes, we learn that the kinetic frictional force is directly proportional to the force compressing the surfaces, and that the proportionality constant does not depend on the size of the surface. Investigate (using at least two pairs of materials) how accurate these statements are.
(6 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'G'Deadline expired on January 15, 2024. |
G. 833. The size of the body of a child in each (linear) direction doubles in a few years. How does the pressure exerted by its feet on the ground changes? (Assume that the density of the child does not change as it grows.)
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 834. We are used to shadows being long in the morning, shortening by midday, lengthening in the afternoon, and then long again at dusk. Is there any place on Earth where the shadow of a vertical stick cast on horizontal ground has the same length all day long?
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 835. A driver is driving at the foot of a hill at \(\displaystyle 60~\mathrm{km/h}\) when he switches to neutral gear. When he reaches the top of the hill, the speedometer of the car reads \(\displaystyle 40~\mathrm{km/h}\). Neglect drag and friction losses.
\(\displaystyle a)\) What would be the speed of the car at the top of the hill if it had reached the bottom of the hill at \(\displaystyle 70~\mathrm{km/h}\)?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What should the minimum speed of the car at the bottom of the hill be in order to reach the top without without using the engine?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 836. An \(\displaystyle \ell=0.5~\mathrm{m}\) long cylindrical glass tube, closed at one end and open at the other, was submerged vertically in the Dead Sea with its open end turned downwards so that the lower (open) end of the tube is at a depth of \(\displaystyle h=30~\mathrm{m}\). Inside the tube there was air at a temperature of \(\displaystyle 32\;{}^\circ\)C and at a pressure of \(\displaystyle 800~\mathrm{mmHg}\) – which was the same as the atmospheric pressure. The water in the Dead Sea has a temperature of \(\displaystyle 27\;{}^\circ\)C and a density \(\displaystyle 1.24\) times that of distilled water. How high does the water rise in the tube?
(4 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'P'Deadline expired on January 15, 2024. |
P. 5526. Starting from rest and accelerating uniformly, a motorcycle travelled \(\displaystyle 13~\mathrm{m}\) in the 7th second of its motion.
\(\displaystyle a)\) How much distance does it cover in the 11th second?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the acceleration of the motorcycle at the end of the 11th second, if its path is a circle with radius \(\displaystyle 120~\mathrm{m}\)?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5527. On a horizontal, rough table, the value of the coefficient of kinetic friction \(\displaystyle \mu\) depends on the distance \(\displaystyle x\) measured from the edge of the table. Launching a small body from the edge at different initial velocities \(\displaystyle v\), we find that the distance along which the small body stops is \(\displaystyle s=kv\), where \(\displaystyle k\) is a parameter characteristic of the table. Determine the function how the value of the coefficient of kinetic friction depends on the position.
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5528. On a horizontal, frictionless surface, a cube of edge \(\displaystyle d=10~\textrm{cm}\) and of uniform mass distribution, is sliding at a velocity of \(\displaystyle v_0\). At some point the cube reaches a slope of an angle of inclination of \(\displaystyle \alpha=30^\circ\). The ``fault line'' between the slope and the ground is perpendicular to the direction of travel of the cube. The front edge of the cube which is in contact with the ground gets stuck at the fault line totally inelastically, so that the cube topples. What is the least value of \(\displaystyle v_0\) if the front face of the cube ``tips'' onto the slope?
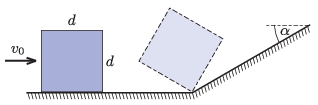
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5529. A 7-tonne helicopter can hover in one place if its engine produces \(\displaystyle 1000~\mathrm{kW}\) of power. Estimate the power required to hover the helicopter in one place if there is an additional 4 tonnes of weight in it.
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5530. The cross sectional area of the piston of a medical syringe is \(\displaystyle 300~\mathrm{mm^2}\) and that of the outlet tube of the syringe is \(\displaystyle 4~\mathrm{mm^2}\). A force of \(\displaystyle 1.4~\mathrm{N}\) is required to move the piston when the device is open (to overcome static friction). After sealing the outlet tube with one finger as shown in the figure, the piston is pushed inwards very slowly with the other finger so that no other part of the syringe is touched (see figure). During the process, the volume of air in the syringe is decreased from \(\displaystyle 20~\mathrm{cm^3}\) to \(\displaystyle 15~\mathrm{cm^3}\).
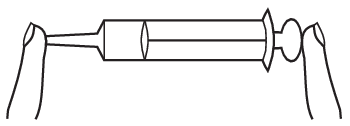
\(\displaystyle a)\) What is the pressure of the air in the syringe after the piston was pushed to its final position?
\(\displaystyle b)\) At this time, what is the least force at which we have to press the end of the outlet tube of the piston?
(The ambient pressure is 100 kPa, the weight of the syringe is negligible.)
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5531. A glowing firefly accidentally flew into the open tube of a Newtonian telescope. When it was moving along the optical axis through point \(\displaystyle P\), which is a point on the principal axis 150 cm from the mirror, the instantaneous speed of its image was twice as fast as when it flew through point \(\displaystyle P\) at the same speed as before, but perpendicularly to the principal axis. What is the focal length of the mirror in the telescope?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5532. A variable capacitor with an initial capacitance of \(\displaystyle C_0\) is charged to a voltage of \(\displaystyle U_0\) and short-circuited through a resistor of resistance \(\displaystyle R\).
\(\displaystyle a)\) How long and how should we vary the capacitance of the capacitor so that the current remains constant when the capacitor is discharged?
\(\displaystyle b)\) Determine the ratio of the initial energy of the capacitor to the heat dissipated by the resistor. Explain your results.
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5533. The \(\displaystyle {}^{40}\mathrm{K}\) isotope has unusual behaviour because it can undergo both negative and positive beta decay, and even capture an inner electron. What is the decay energy of the three processes in MeV units?
Hint: For the relative isotopic masses see https://www.komal.hu/cikkek/atomtomegek.pdf\,.
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5534. The \(\displaystyle x\)-axis of a Cartesian coordinate system is horizontal and the \(\displaystyle y\)-axis is vertical. Connect each point \(\displaystyle x=\xi\) of the \(\displaystyle x\) axis, \(\displaystyle 0\le \xi\le h=1~\mathrm{m}\), to the point \(\displaystyle y=h-\xi\) on the \(\displaystyle y\) axis. The yellow region in the figure shows the above defined line segments. Lay a frictionless, thin tube along the envelope of the line segments.
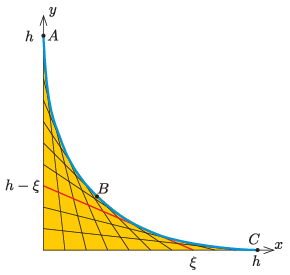
Launch a small body of mass \(\displaystyle m\) from the top of the tube without any initial speed. Determine the force in \(\displaystyle mg\) units with which the body pushes the wall of the tube during its motion
\(\displaystyle a)\) right after its start at point \(\displaystyle A\);
\(\displaystyle b)\) at point \(\displaystyle B\), which is the midpoint of the tube;
\(\displaystyle c)\) at point \(\displaystyle C\), which is a point right before the body leaves the tube.
(6 pont)
Upload your solutions above.
