KöMaL Problems in Physics, January 2024
Please read the rules of the competition.
Show/hide problems of signs:
 |
Problems with sign 'M'Deadline expired on February 15, 2024. |
M. 428. Measure how much power is required to heat water in a microwave oven. What can this value depend on?
(6 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'G'Deadline expired on February 15, 2024. |
G. 837. Consider the liquid and gaseous phases of water at \(\displaystyle 100~{}^\circ\text{C}\) and at atmospheric pressure. On average, how many times farther apart are the centres of adjacent water molecules in the vapour phase than in the liquid phase?
(3 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 838. In the photo, taken from a drone, and shown below, people walk on the level ground along the riverbank of Rio Grande at the border between Mexico and the United States. Estimate how high the Sun was when the photo was taken.

(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 839. Two motorcycles are travelling behind each other at a speed of \(\displaystyle 30~\text{m/s}\) on a racetrack, the distance between them is \(\displaystyle 23~\text{m}\), and the length of the motorcycles is \(\displaystyle 2~\text{m}\). At some point, the motorcyclist at the back starts overtaking the other, he accelerates at \(\displaystyle 1~\text{m}/\text{s}^2\) until he is \(\displaystyle 23~\text{m}\) ahead the other, and then continues at a constant speed. At the moment he finishes overtaking, the other rider starts overtaking him at an acceleration of \(\displaystyle 1~\text{m}/\text{s}^2\), which he also finishes \(\displaystyle 23~\text{m}\) ahead the other motorcyclist. What are the speeds of the motorcyclists after this double overtaking?
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
G. 840. What is the minimum speed of a room-temperature lead ball at which it must hit a wall in order that it melts? Assume that half of the heat released during the inelastic collision heats the wall and half heats the lead ball.
(4 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'P'Deadline expired on February 15, 2024. |
P. 5535. The surface of a \(\displaystyle 2~\text{m}^2\) shade sail is nearly horizontal. Suddenly, it starts raining at a steady pace. There is a small hole in the middle of the sail through which the rainwater flows off. A cylindrical container, which has a hole of cross section \(\displaystyle 5~\text{mm}^2\) at its bottom, is placed under the jet of water. The rise of the water level in the container stops at \(\displaystyle 20~\text{cm}\). Determine how many mm of precipitation fell during the 10 minutes of rain.
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5536. In a football match, a free kick is taken from a point \(\displaystyle P\) at a distance \(\displaystyle d\) from the goal. Point \(\displaystyle P\) is on the perpendicular bisector of the goal line. The player kicks the ball at an angle of \(\displaystyle \alpha\) just towards the centre of the upper goalpost, but after a time \(\displaystyle t_1\) it falls to the ground in the middle of the goal line. The kick has to be repeated for some reason. The second time, the player kicks the ball harder, at an angle of \(\displaystyle 2\alpha\), and after \(\displaystyle t_2\) it hits the middle of the top goalpost. (The size of the goal is slightly different from the regular size of a goal.)
\(\displaystyle a)\) What was the angle \(\displaystyle \alpha\)?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What was the distance \(\displaystyle d\)?
\(\displaystyle c)\) What were the initial speeds of the ball at the first and at the second kick?
(Consider the ball as a point-like body and neglect air resistance.)
Data: \(\displaystyle t_1=1.90~\text{s}\), \(\displaystyle t_2=1.93~\text{s}\), \(\displaystyle g=9.81~\text{m}/\text{s}^2\).
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5537. In an adventure park, adventurers can roll down freely (without brakes) in a small car from point \(\displaystyle A\), which is at the top of a \(\displaystyle R=20~\text{m}\) high slope. The slope has an \(\displaystyle \alpha=30^{\circ}\) inclination angle, the car's initial speed is zero. The slope is connected smoothly to a circular arc-shaped track of radius \(\displaystyle R\) at point \(\displaystyle B\), then the track continues horizontally from its lowest point \(\displaystyle C\). On the horizontal part of the track, the car is properly braked, decelerates uniformly in time, and stops at \(\displaystyle D\) after covering a distance of \(\displaystyle \ell=2R\).
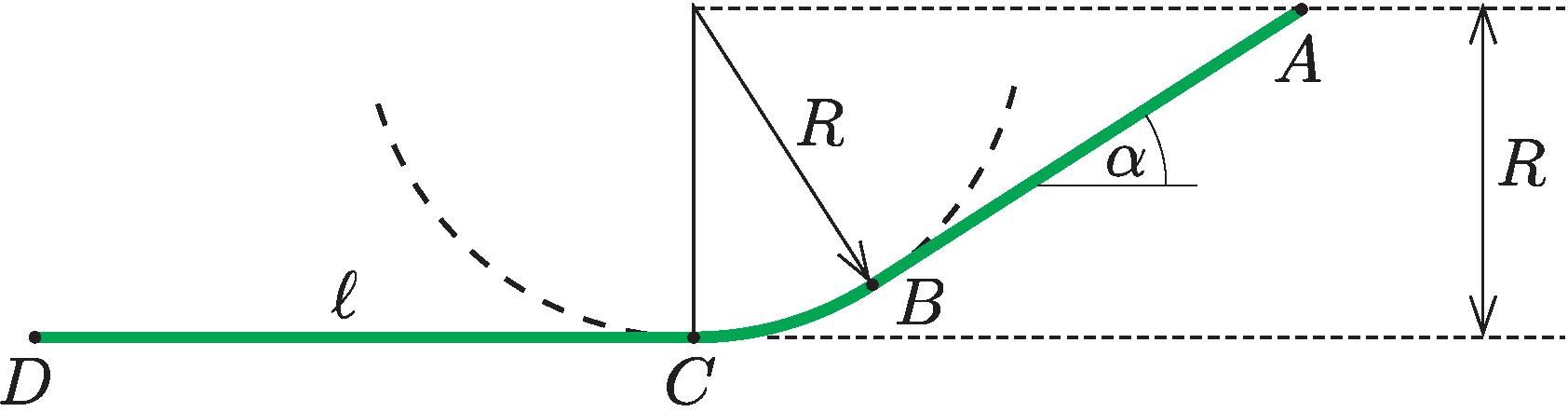
Calculate how many times the their normal weight do the passengers in the car feel during the motion. Graph this ratio as a function of the travelled distance.
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5538. In many playgrounds you will find a rotating climbing frame similar to the one in the figure. On such a climbing frame, an ant climbs up while the frame is rotating uniformly. The upward climbing ant constantly feels that it is climbing ``vertically upwards''.
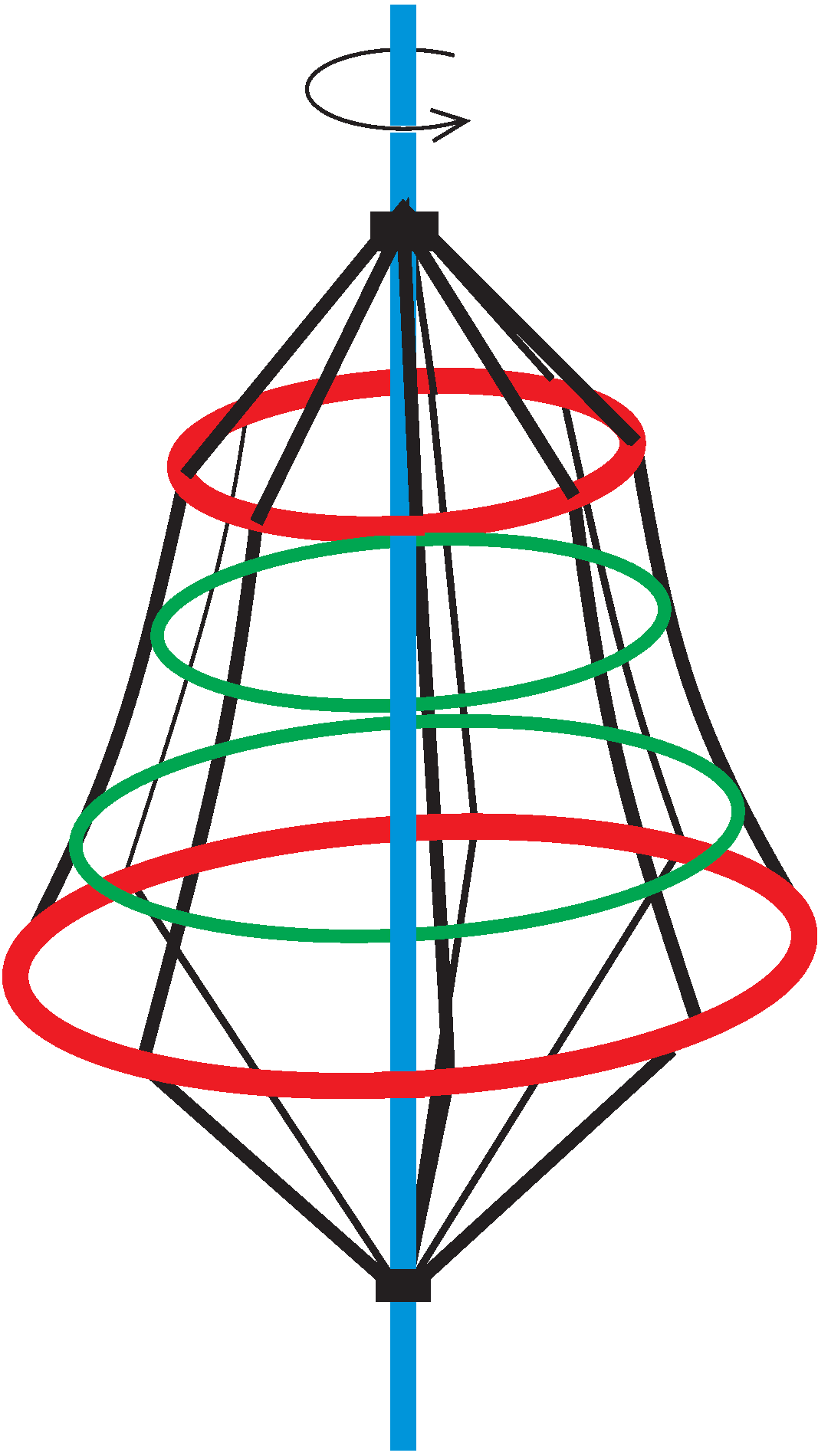
The radius of the lower red circular ring that hold the ropes of the climbing frame is \(\displaystyle 2~\text{m}\), whilst the upper red ring has a radius of \(\displaystyle 1~\text{m}\). The distance between the rings is \(\displaystyle 3~\text{m}\). What is the angular speed of the climbing frame?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5539. A long, rigid plank of negligible mass is suspended by \(\displaystyle n\) equally spaced springs of the same spring constants, and the same unstretched lengths. The first spring can exert a maximum force of \(\displaystyle K\), the second can exert a maximum force of \(\displaystyle 2K\), \(\displaystyle \ldots\), the \(\displaystyle n^\text{th}\) a force of \(\displaystyle n\cdot K\) without breaking. What is the maximum mass of a body that can be placed on the plank? Where should it be placed? (Assume that the springs are barely stretched.)
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5540. Two glasses, which have the same size are filled with room-temperature tea, then one of them is placed into the refrigerator, and the other into the much colder freezer. After a minute elapsed, the glasses are swapped, and left in their new places for a further minute and then both are removed. The content of which glass will cool down more during the experiment? Newton's law of cooling can be applied to the relevant heat transfer processes, and the heat transfer coefficient can be considered to be the same for the refrigerator and the freezer.
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5541. \(\displaystyle ^{222}\text{Rn}\) is a member of the uranium-radium decay series: it is an alpha decaying isotope with a half-life of \(\displaystyle 3.8\) days.
\(\displaystyle a)\) If the radon nucleus in transition is assumed to be at rest, what is the speed of its daughter product?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the energy of the alpha particle produced in the decay in MeV?
Hint: See the isotopic masses at https://www.komal.hu/cikkek/atomtomegek.pdf
(4 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5542. From a resistor of resistance \(\displaystyle R\), a coil of inductance \(\displaystyle L\), a capacitor of capacitance \(\displaystyle C\) and a generator with voltage \(\displaystyle U(t)=U_0\sin(\omega t)\) we build the simple circuit shown in the figure.
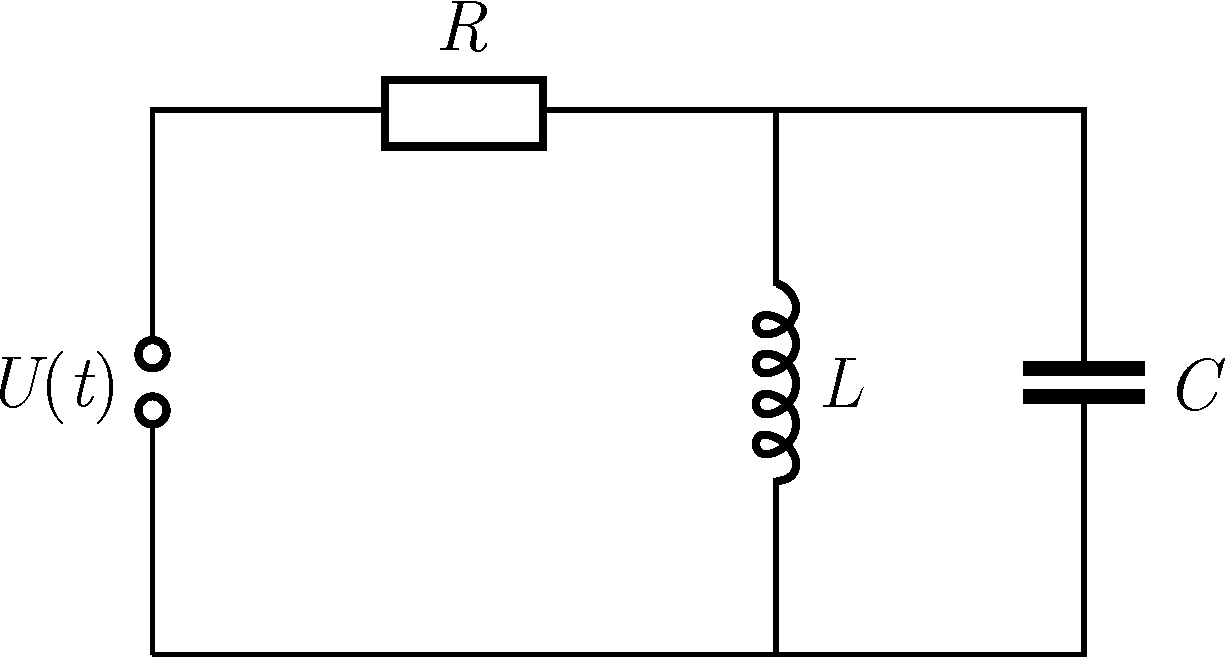
\(\displaystyle a)\) What is the amplitude of the current flowing through the resistor?
\(\displaystyle b)\) How should we choose the angular frequency \(\displaystyle \omega\) in order that no current should flow through the resistor?
(5 pont)
solution (in Hungarian), statistics
P. 5543. In cloudy weather, measurements are taken with a light meter pointed towards the sky. We find that, due to the scattering of light by the clouds, the incident power per unit area is approximately \(\displaystyle I_0\), regardless of the orientation of the light meter. On top of an opaque thin-walled spherical shell of radius \(\displaystyle R\), there is a small hole of radius \(\displaystyle r\) (much larger than the wavelength of visible light). The inner side of the wall of the spherical shell is coated with soot. Give the intensity of illumination on the inner surface of the shell, which is placed in the open air.
(6 pont)
Upload your solutions above.
