KöMaL Problems in Physics, April 2024
Please read the rules of the competition.
Show/hide problems of signs:
 |
Problems with sign 'M'The deadline is: May 15, 2024 24:00 (UTC+02:00). |
M. 431. Measure the refractive index of gelatine.
(6 pont)
 |
Problems with sign 'G'The deadline is: May 15, 2024 24:00 (UTC+02:00). |
G. 849. How long would a day on Earth be if there was weightlessness on the equator? Assume that all parameters other than the period of rotation are constant.
(3 pont)
This problem is for grades 1–10 students only.
G. 850. What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit shown in the figure between the two terminals of the battery?
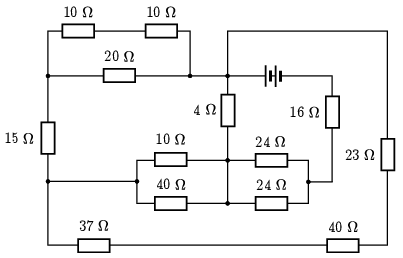
(4 pont)
This problem is for grades 1–10 students only.
G. 851. The refractive index of zirconia (zirconium-dioxide) is \(\displaystyle 2.1\). A prism of angles \(\displaystyle 30^\circ-60^\circ-90^\circ\) is made from this material on which two thin rays of light are incident as shown in the figure. What is the angle between the two rays of light emerging from the prism?
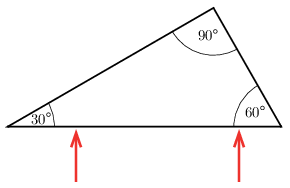
(4 pont)
This problem is for grades 1–10 students only.
G. 852. A radioactive sample contains two different isotopes, denoted by A and B. The half-life of isotope A is 3 days and that of isotope B is 6 days. Initially, there are twice as many atoms in isotope A then in isotope B. In what time will this ratio reverse to its reciprocal?
(4 pont)
This problem is for grades 1–10 students only.
 |
Problems with sign 'P'The deadline is: May 15, 2024 24:00 (UTC+02:00). |
P. 5562. From one edge of a horizontal table, a point-like body is launched with an initial speed of \(\displaystyle v_0\). The body slides along the surface of the table, then flies off the table and hits the ground at the speed of \(\displaystyle v_0\), the angle between this final velocity and the horizontal is \(\displaystyle \alpha=30^\circ\). The table is \(\displaystyle h=0.8~\mathrm{m}\) high and \(\displaystyle \ell=3.2~\mathrm{m}\) long (see the figure).
\(\displaystyle a)\) What was the initial speed of the object?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the table and the body?
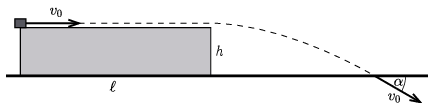
(4 pont)
P. 5563. Small bodies of masses \(\displaystyle M\) and \(\displaystyle m\) are connected with a thread of length \(\displaystyle \ell\). We attach another thread to the body of mass \(\displaystyle M\) and move the other, upper end of this thread horizontally such that this upper end executes a small amplitude simple harmonic motion of period \(\displaystyle T\). (See figure.) For what length \(\displaystyle \ell\) can the oscillating thread remain vertical all the time?
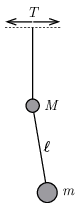
(5 pont)
P. 5564. A ping pong ball rests on a horizontal ping pong racket. The racket is moved in the horizontal direction so that it undergoes simple harmonic motion. The initial velocity is zero, the amplitude is \(\displaystyle A\) and the angular frequency is \(\displaystyle \omega\). Give the displacement of the ball's centre as a function of time. What is the length of the trail left by the ball on the racket if the ball's surface was covered with graphite? (Assume that the ball does not leave the surface of the racquet and does not slide on it.)
(5 pont)
P. 5565. One end of a long, flexible, heavy chain was fixed. The hanging chain would break if a load greater than the weight of the chain was hung on it. The chain is released from the position shown in the figure. (Both the moving and the already taut parts of the chain can be considered to be vertical.) Will the chain break?
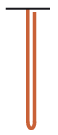
(5 pont)
P. 5566. There are two discs of radii \(\displaystyle 2r\) and \(\displaystyle r\) at rest on a horizontal, not perfectly flat tabletop such that they almost touch each other. In the plane, a third disk of radius \(\displaystyle 3r\) slides without rotation so that its velocity vector is parallel to the common tangent of the three disks. The top view of the three disks are shown in the figure. All three disks are made of the same material and have the same height. After the collision, which is considered to be elastic, the disc with radius \(\displaystyle 3r\) slows down due to friction and stops after travelling \(\displaystyle d=5~\mathrm{cm}\). In what direction and how far will the smaller discs travel on the table? Friction between the discs is negligible. Hint: See problem P. 5555. in the March 2024 issue of this journal and the article titled Complex numbers in physics I. in this issue.
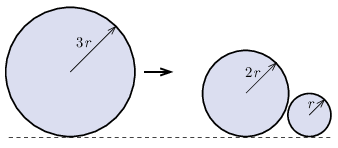
(5 pont)
P. 5567. An insulated tank of height \(\displaystyle h\) is placed into vacuum and stands on a horizontal table. The tank has a rim as shown. The tank initially contains a sample of gas at pressure \(\displaystyle p_0\), and is sealed at the top by an insulating light piston, and also at the middle of the tank there is a thin, light piston made from some heat conducting material (see figure). The upper half part of the tank contains a sample of monatomic gas, and in the lower half part there is a sample of diatomic gas. A very heavy load is carefully placed on the upper piston and then released. The movement of the pistons stops after a few oscillations due to the internal friction of the gases. Where are the pistons in their equilibrium position?
(5 pont)
P. 5568. In two circular regions of radius \(\displaystyle R\) at a distance of \(\displaystyle d\) (\(\displaystyle d>2R\)) from each other (two black circles), there is uniform magnetic field of magnetic induction \(\displaystyle B\) which points in the same direction, perpendicular to the plane of the figure. A point particle with charge \(\displaystyle Q\) and mass \(\displaystyle m\) moves periodically at a speed of \(\displaystyle v\) along the orbit shown in the figure (red curve). How long does it take for the particle to cover the red orbit once? What is the minimum value of the magnetic induction so that the particle still moves periodically along an orbit?
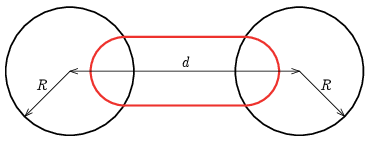
(4 pont)
P. 5569. Estimate the ratio of the number of protons to that of neutrons in the human body.
(3 pont)
P. 5570. The circuit – containing three identical resistors and two identical coils – shown in the figure has been connected to a DC source for a relatively long time. (The resistance of the coils is negligible.)
\(\displaystyle a)\) What will be the current flowing through the resistors immediately after switch K is turned off?
\(\displaystyle b)\) What is the value of the induced electromotive force in each coil, right after switch K is turned off?
\(\displaystyle c)\) How do the sum and difference of the currents in the coils vary in time?
\(\displaystyle d)\) How long does it take for the current in one coil and the current in the other coil to drop to half of the current measured very soon after switch K was turned off?
Data: \(\displaystyle U_0=1~\mathrm{V}\), \(\displaystyle L=1~\mathrm{H}\), \(\displaystyle R=1\,\Omega\).
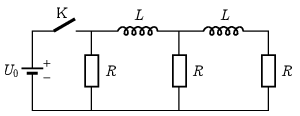
(6 pont)
Upload your solutions above.
