 Problem P. 4953. (September 2017)
Problem P. 4953. (September 2017)
P. 4953. Some argon gas is put into a Torricelli-tube of length \(\displaystyle L=1\) m and of cross section \(\displaystyle A=2\) cm\(\displaystyle {}^2\), therefore the height of the mercury in the tube is only \(\displaystyle h_1=0.4\) m. The ambient air pressure is \(\displaystyle p_0=10^5\) Pa, and the initial temperature is 20 \(\displaystyle {}^\circ\)C.
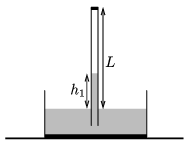
\(\displaystyle a)\) What is the mass of the argon gas above the mercury?
\(\displaystyle b)\) The temperature of the gas is slowly increased. What is the temperature of the gas when the height of the mercury in the tube is \(\displaystyle h_2=0.36\) m?
\(\displaystyle c)\) How much work was done by the extending gas during the process?
(5 pont)
Deadline expired on October 10, 2017.
Sorry, the solution is available only in Hungarian. Google translation
Megoldás. \(\displaystyle a)\) Az argongáz nyomása
\(\displaystyle p_1=p_0-\varrho g h_1=4{,}7\cdot 10^4~\rm Pa,\)
térfogata
\(\displaystyle V_1=A(L-h_1)=1{,}20\cdot10^{-4}~\rm m^3.\)
A gáz tömege az egyesített gáztörvény szerint
\(\displaystyle m=\frac{p_1V_1}{RT_1}M=\frac{(4{,}7\cdot 10^4)\cdot (1{,}2\cdot10^{-4})}{8{,}3\cdot 293}\, 40~{\rm g}\approx 93~{\rm mg}.\)
\(\displaystyle b)\) A felmelegített gáz nyomása
\(\displaystyle p_2=p_0-\varrho g h_2=5{,}3\cdot 10^4~\rm Pa,\)
térfogata
\(\displaystyle V_2=A(L-h_2)=1{,}28\cdot10^{-4}~\rm m^3.\)
A megváltozott hőmérséklet a gáztörvény szerint
\(\displaystyle T_2=T_1\frac{p_2V_2}{p_1V_1}=352~\rm K=79\,^\circ\rm C.\)
\(\displaystyle c)\) Könnyen belátható, hogy a gáz nyomása a térfogat változása során lineárisan változik. (Mivel a cső keresztmetszete állandó, a higanyoszlop magassága, ami a külső légnyomás és az argongáz nyomásának különbségével arányos, a higany térfogatával, vagyis a kilógó cső térfogatának és a gáz térfogatának különbségével arányos.) A lineáris \(\displaystyle p(V)\) kapcsolat miatt a munkavégzés számolható a
\(\displaystyle \bar{p}=\frac{p_1+p_2}{2}=5{,}0\cdot 10^4~\rm Pa \)
átlagos nyomásból. Mivel a térfogatváltozás
\(\displaystyle \Delta V= (h_1-h_2)A=8\cdot10^{-6}~\rm m^3,\)
a gáz által végzett munka
\(\displaystyle W=\bar{p}\,\Delta V=0{,}4~\rm J.\)
Statistics:
114 students sent a solution. 5 points: 64 students. 4 points: 24 students. 3 points: 7 students. 2 points: 12 students. 1 point: 6 students. 0 point: 1 student.
Problems in Physics of KöMaL, September 2017
